Free Access
| Issue |
Environ. Biosafety Res.
Volume 4, Number 2, April-June 2005
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 89 - 102 | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/ebr:2005016 | |
| Published online | 15 November 2005 | |
- Advisory Committee on Releases to the Environment's (ACRE’s) response to concerns raised in written representations and submissions associated with the CHARDON LL public hearing and to statements made at ACRE’s open hearing relating to the safety assessment of T25 GM maize conducted under Directive 90/220/EEC. (2002) http://www.defra.gov.uk/environment/acre/advice/pdf/acre_advice20.pdf [Google Scholar]
- Alonso J, Barredo JL, Diez B, Mellado E, Salto F, Garcia JL, Cortes E (1998) D- Amino-acid oxidase gene from Rhodotorula gracilis (Rhodosporidium toruloides) ATCC 26217. Microbiology 144: 1095–1101 [Google Scholar]
- Aragão FJL, Brasileiro ACM (2002) Positive, negative and marker-free strategies for transgenic plant selection. Braz. J. Plant Physiol. 14: 1–10 [Google Scholar]
- Astwood JD, Fuchs RL (1996) Allergenicity of foods derived from transgenic plants. In Wuthrich B, Ortolani C, eds, Highlights in Food Allergy, Monogr. Allergy 32: 105–120 [Google Scholar]
- Australia New Zealand Food Authority (2001) Food derived from insect protected (New Leaf®) Potato lines BT-06, ATBT04-06, ATBT04-31, ATBT04-36,and SPBT02-05; A Safety Assessment. Technical Report Series No. 11 [Google Scholar]
- Beck E, Ludwig G, Auerswald EA, Reiss B, Schaller H (1982) Nucleotide sequence and exact localization of the neomycin phosphotransferase gene from transposon Tn5. Gene 9: 327–336 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan MW, Flavell RB, Chilton M-D (1983) A chimaeric antibiotic resistance gene as a selectable marker for plant cell transformation. Nature 304: 184–187 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Brasileiro ACM, Aragão FJL (2001) Marker genes for in vitro selection of transgenic plants. J. Plant Biotechnol. 3: 113–121 [Google Scholar]
- Canadian Food Inspection Agency, Plant Health and Production Division, Decision Document DD98-28 (1998) Determination of the Safety of AgrEvo Canada Inc.'s Glufosinate Ammonium Herbicide-Tolerant Brassica rapa Canola Line HCR-1. http://www.inspection.gc.ca/english/plaveg/bio/dd/dd9828e.shtml [Google Scholar]
- Canadian Food Inspection Agency, Plant Products Directorate Plant Biosafety Office, Decision Document DD2004-49 (2004) Determination of the Safety of Bayer CropScience's Herbicide Tolerant LibertyLink® Cotton Event LLcotton25 (Gossypium hirsutum L.). http://www.inspection.gc.ca/english/plaveg/bio/dd/dd0449e.shtml [Google Scholar]
- Cellini F, Chesson A, Colquhoun I, Constable A, Davies HV, Engel KH, Gatehouse AMR, Karenlampi S, Kok EJ, Leguay J-J, Lehesranta S, Noteborn HPJM, Pedersen J, Smith M (2004) Unintended effects and their detection in genetically modified crops. Food Chem. Toxicol. 42: 1089–1125 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalfie M (1995) Green Fluorescent Protein. Photochem. Photobiol. 62: 651–656 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalfie M, Tu Y, Euskirchen G, Ward WW, Prasher DC (1994) Green fluorescent protein as a marker for gene expression. Science 263: 802–805 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavarriaga P (2005) Personal communication [Google Scholar]
- Codex Alimentarius Commission Alinorm 03/34, Joint FAO/WHO Food Standard Programme Codex Alimentarius Commission, Twenty-fifth session, Rome Italy (2003) Report of the Third Session of the CODEX Ad Hoc Intergovernmental Task Force on Foods Derived From Biotechnology, Yokohama, Japan 4–8 March 2002. Appendix IV:57-60. http://www.codexalimentarius.net/download/report/46/Al0334ae.pdf [Google Scholar]
- DeBlock M, De Brower D, Tenning P (1989) Transformation of Brassica napus and Brassica oleracea using Agrobacterium tumefaciens and the expression of the bar and neo genes in the transgenic plants. Plant Physiol. 91: 694–701 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vetten N, Wolters AM, Raemakers K, van der Meer I, ter Stege R, Heeres E, Heeres P, Visser R (2003) A transformation method for obtaining marker-free plants of a cross-pollinating and vegetatively propagated crop. Nat. Biotechnol. 21: 439–442 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) (1997) Phosphinothricin Acetyltransferase and the Genetic Material Necessary for Its Production in All Plants; Exemption from the Requirement of a Tolerance on All Raw Agricultural Commodities. Federal Register 62: 17717–17720 [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) (2004a) Hygromycin B phosphotransferase; exemption from the requirement of a tolerance. Federal Register 69: 18275–18278 [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) (2004b) Phosphomannose Isomerase and the Genetic Material Necessary for Its Production in All Plants; Exemption from the Requirement of a Tolerance. Federal Register 69: 26770–26775 [Google Scholar]
- Erikson O, Clapham D, Hertzberg M, Näsholm T (2003) D- Amino acid selectable markers. Online abstract at http://www.treebiotech2003.norrnod.se/s2_o.htm accessed 1/27/2005 [Google Scholar]
- Erikson O, Hertzberg M, Näsholm T (2004) A conditional marker gene allowing both positive and negative selection in plants. Nat. Biotechnol. 22: 455–458 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- European Federation of Biotechnology (2001) Antibiotic resistance markers in genetically modified GM crops. Briefing Paper 10 http://www.efbweb.org/public/pubview.htm site access 12/16/2004 [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority (2004) Opinion of the Scientific Panel on Genetically Modified Organisms on the use of antibiotic resistance genes as marker genes in genetically modified plants (Question N EFSA-Q-2003-109) Opinion adopted on 2 April 2004 The EFSA Journal 48:1-18 [Google Scholar]
- Food and Drug Administration (1994) “Secondary Food Additives Permitted in Food for Human Consumption; Food Additives Permitted in Feed and Drinking Water of Animals; Aminoglycoside 3'-Phosphotransferase II; Final Rule.” Federal Register 59:26700-26711 [Google Scholar]
- Food and Drug Administration Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition Office of Premarket Approval (1998) Guidance for Industry: Use of Antibiotic Resistance Marker Genes in Transgenic Plants Draft Guidance. http://vm.cfsan.fda.gov/~dms/opa-armg.html [Google Scholar]
- Food Standards Australia New Zealand (2002) Final assessment report application A436. Oil and linters derived from insect protected cotton containing event 15985. http://www.foodstandards.gov.au/standardsdevelopment/applications/applicationa436insectprotectedcotton/a436farexecsummary211633.cfm [Google Scholar]
- Fraley RT, Rogers SG, Horsch RB, Sanders PR, Flick JS, Adams SP, Bittner ML, Brand LA, Fink CL, Fry JS, Gallupi GR, Goldberg SB, Hoffman NL, Woo SC (1983) Expression of bacterial genes in plant cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA) 80: 4803–4807 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Fregene M, Puonti-Kaerlas J (2002) Cassava Biotechnology. In Hillocks RJ, Thresh JM, Bellotti AC, eds, Cassava: Biology, Production and Utilization, CAB International, pp 179–207 [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs RL, Ream JE, Hammond BG, Naylor MW, Leimgruber RM, Berberich SA (1993) Safety assessment of the neomycin phosphotransferase II (NPTII) protein. Biotechnology 11: 1543–1547 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
-
Gilissen LJW, Metz PLJ, Stiekema WJ, Nap JP (1998) Biosafety of E. coli
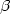 -glucuronidase (GUS) in plants. Transgenic Res. 7: 157–163
[CrossRef]
[PubMed]
[Google Scholar]
-glucuronidase (GUS) in plants. Transgenic Res. 7: 157–163
[CrossRef]
[PubMed]
[Google Scholar]
- Goldsbrough A (2001) Methods for avoidance and removal of selectable marker genes in crop transformation systems. http://www.defra.gov.uk/environment/acre/uti/08.htm [Google Scholar]
- González AE, Schöpke C, Taylor NJ, Beachy RN, Fauquet CM (1998) Regeneration of transgenic cassava plants (Manihot esculenta Crantz) through Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of embryogenic suspension cultures. Plant Cell Rep. 17: 827–831 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Gritz L, Davies J (1983) Plasmid-encoded hygromycin B resistance: the sequence of hygromycin B phosphotransferase gene and its expression in Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene 25: 179–188 [Google Scholar]
- Hails RS (2000) Genetically modified plants – The debate continues. Trends Ecol. Evol. 15: 14–18 [Google Scholar]
- Haseloff J, Amos B (1995) GFP in Plants. Trends Genet. 11: 328–329 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslberger AG (2003) Codex Guidelines for GM Foods Include the Analysis of Unintended Effects. Nat. Biotechnol. 21: 739–741 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera-Estrella L, De Block M, Messens E, Hernalsteen JP, Van Montagu M, Schell J (1983) Chimeric genes as dominant selectable markers in plant cells. EMBO J. 2: 987–995 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Information Systems for Biotechnology, Field Test Releases in the U.S. Updated 12/22/2004 http://www.isb.vt.edu/cfdocs/fieldtests1.cfm accessed 12/27/2004 [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson RA (1989) The GUS reporter gene system. Nature 342: 837–838 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelenic S (2003) Kanamycin Resistance Marker Gene in Transgenic Plants. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 41: 183–190 [Google Scholar]
- Jennings DL, Iglesias C (2002) Breeding for Crop Improvement. In Hillocks RJ, Thresh JM, Bellotti AC, eds, Cassava: Biology, Production and Utilization, CAB International, pp 149–166 [Google Scholar]
- Jones DD, Maryanski JH (1991) Safety considerations in the evaluation of transgenic plants for human food. In Levin MA, Straus HS, eds, Risk Assessment in Genetic Engineering, New York: McGraw-Hill, pp 64–82 [Google Scholar]
- Kärenlampi S (1996) Health Effects of Marker Genes in Genetically Engineered Food Plants. TemaNord 530. The Nordic Council of Ministers. Store Standstræde 18. DK-1255 Copenhagen K, pp 7–66 [Google Scholar]
- Kopertekh L, Jüttner G, Schiemann J (2004) PVX-Cre-mediated marker gene elimination from transgenic plants. Plant Mol. Biol. 55: 491–500 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhstoss S, Rao RN (1983) Expression in Streptomyces ambofaciens of an Escherichia coli K-12 gene which confers resistance to hygromycin B. Gene 26: 295–299 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laminski S, Gray VM, Mycock DJ, Blatch GL, Groll J, Rey MEC (2002) Green fluorescent protein as a reporter of early transformation in Cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz). South African J. Sci. 98: 301–303 [Google Scholar]
- Leboul J, Davies J (1982) Enzymatic modification of hygromycin B in Streptomyces hygroscopicus. J. Antibiot. 35: 527–528 [Google Scholar]
- Li HQ, Sautter C, Potrykus I, Pounti-Kaerlas J (1996) Genetic transformation of cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz). Nat. Biotechnol. 14: 736–740 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malpartida F, Zalacain M, Jimenez A, Davies J (1983) Molecular cloning and expression in Streptomyces lividans of a hygromycin B phosphotransferase gene from Streptomyces hygroscopicus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 117: 6–12 [Google Scholar]
- Marker Genes Technologies, Inc., Live cell luciferase assay kit – Product Mo626 Product Information Sheet (0626-005). http://www.markergene.com/ [Google Scholar]
- Matthews P, Fieg S, Gubler F, McCallum G, McCarthy N, Thornton S, Wang M, Jacobsen J (1999) Transgene Segregation to Obtain Selectable Marker-Free Transformed Barley. Proceedings of the 9th Australian Barley Technical Symposium. http://www.regional.org.au/au/abts/1999/matthews. htm?PHPSESSID=ec4a0c42626ab4dc068f9be832936974#P0_0 [Google Scholar]
- Miki B, McHugh S (2004) Selectable marker genes in transgenic plants: applications, alternatives and biosafety. J. Biotechnol. 107: 193–232 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles JS, Guest JR (1984) Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional start point of the phosphomannose isomerase gene (manA) of Escherichia coli. Gene 32: 41–48 [Google Scholar]
- Millar AJ, Short SR, Hiratsuka K, Chua NH, Kay SA (1992) Firefly luciferase as a reporter of regulated gene expression in higher plants. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 10: 324–337 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Monsanto Company web site: http://www.monsanto.com/monsanto/content/sci_tech/prod_safety/bollgard_II/pss.pdf August 2003 accessed 12/23/2004 [Google Scholar]
- Nap JP, Bijvoet J, Stiekema WJ (1992) Biosafety of kanamycin-resistant transgenic plants. Transgenic Res. 1: 239–249 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- National Academy of Sciences (NAS) (2000) Genetically modified pest-protected plants: Science and regulation, Washington D.C.: National Academy Press [Google Scholar]
- National Academy of Sciences (NAS) (2002) Environmental effects of transgenic plants, Washington D.C.: National Academy Press [Google Scholar]
- OECD Environmental Health and Safety Publications Series on Harmonization of Regulatory Oversight in Biotechnology No. 11 (1999) Consensus Document on General Information Concerning the Genes and Their Enzymes that Confer Tolerance to Phosphinothricin Herbicide. http://www.olis.oecd.org/olis/1999doc.nsf/LinkTo/env-jm-mono(99)13 [Google Scholar]
- Office of the Gene Technology Regulator (2003) Risk Assessment and Risk Management Plan Application for license for dealings involving intentional release of a genetically modified organism into the environment. DIR 034/2003 Title: Field Trial of Genetically Modified Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) Expressing an Insecticidal Gene (vip3A) http://www.ogtr.gov.au/pdf/ir/dir034.pdf [Google Scholar]
- Olsen KM, Schaal BA (1999) Evidence on the origin of cassava: Phylogeography of Manihot esculenta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA) 96: 5586–5591 [Google Scholar]
- Ouakfaoui S, Miki B (2005) The stability of the Arabidopsis transcriptome in transgenic plants expressing the marker genes nptII and uidA. Plant J. 41: 791–800 [Google Scholar]
- Ow DW (2002) Recombinase-directed plant transformation for the post-genomic era. Plant Mol. Biol. 48: 183–200 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ow DW, Wood KV, DeLuca M, De Wet JR, Helinski DR, Howell SH (1986) Transient and stable expression of the firefly luciferase gene in plant cells and transgenic plants. Science 234: 856–859 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang S-Z, DeBoer D, Wan Y, Ye G, Layton JC, Neher MK, Armstrong CL, Fry JE, Hinchee MAW, Fromm ME (1996) An improved Green Fluorescent Protein gene as a vital marker in plants. Plant Physiol. 112: 893–900 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardo JM, Malpartida F, Rico M, Jimenez A (1985) Biochemical basis of resistance to hygromycin B in Streptomyces hygroscopicus – the producing organism. J. Gen. Microbiol. 131: 1289–1298 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalle LS (2002) Phosphomannose isomerase, a novel plant selection system: potential allergenicity assessment. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 964: 129–138 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalle LS, Wright M, Reed J, Hansen G, Dawson J, Dunder EM, Chang Y-F, Powell ML, Meghji M (2000) Phosphomannose Isomerase, A Novel Selectable Plant Selection System: Mode of Action and Safety Assessment. In Fairbairn C, Scoles G, McHughen A, eds, Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on The Biosafety of Genetically Modified Organisms, Saskatoon, Canada, University Extension Press, Univ. Saskatchewan, pp 171–178 [Google Scholar]
- Raemakers CJJM, Sofiari E, Taylor N, Henshaw G, Jacobsen E, Visser RGF (1996) Production of transgenic cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) plants by particle bombardment using luciferase activity as selection marker. Mol. Breed. 2: 339–349 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Raemakers CJJM, Sofiari E, Jacobsen E, Visser RGF (1997) Regeneration and transformation of cassava. Euphytica 96: 153–161 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Raemakers K, Schreuder M, Pereira I, Munyikwa T, Jacobsen E, Visser R (2001) Progress made in FEC transformation of cassava. Euphytica 120: 15–24 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Rao RN, Allen NE, Hobbs JN Jr., Alborn WE Jr., Kirst HA, Paschal JW (1983) Genetic and enzymatic basis of hygromycin B resistance in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 24: 689–695 [Google Scholar]
- Redenbaugh K, Hiatt W, Martineau B, Lindemann J, Emlay D (1994) Aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase II (APH (3') II): Review of its safety and use in the production of genetically engineered plants. Food Biotechnol. 8: 137–165 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J, Privalle LS, Powell ML, Meghji M, Dawson J, Dunder E, Suttie J, Wenke A, Launis K, Kramer C, Chang YF, Hansen G, Wright M (2001) Phosphomannose isomerase: An efficient selectable marker for plant transformation. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 37: 127–132 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Richards HA, Han CT, Hopkins RG, Failla ML, Ward WW, Stewart CN (2003) Safety assessment of recombinant green fluorescent protein orally administered to weaned rats. J. Nutr. 133: 1909–1912 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarria R, Torres E, Angel F, Chavarriaga P, Roca WM (2000) Transgenic plants of cassava (Manihot esculenta) with resistance to Basta obtained by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Plant Cell Rep. 19: 339–344 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Schöpke C, Taylor N, Carcamo R, Konan NK, Marmey P, Henshaw GG, Beachy RN, Fauquet CM (1996) Regeneration of transgenic cassava plants (Manihot esculenta Crantz) from microbombarded embryogenic suspension cultures. Nat. Biotechnol. 14: 731–735 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siritunga D, Sayre RT (2003) Generation of cyanogen-free transgenic cassava. Planta 217: 367–373 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjoblad RD, McClintock JT, Engler R (1992) Toxicological considerations for protein components of biological pesticide products. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 15: 3–9 [Google Scholar]
- Smalla K, Borin S, Heuer H, Gebhard F, van Elsas JD, Nielsen K (2000) Horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance genes from transgenic plants to bacteria – are there new data to fuel the debate? In Fairbairn C, Scoles G, McHughen A, eds, Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on The biosafety of genetically modified organisms, Saskatoon, Canada, University Extension Press, Univ. Saskatchewan, pp 146–154 [Google Scholar]
- Stewart CN, Richards HA, Halfhill MD (2000) Transgenic Plants and Biosafety: Science, Misconceptions and Public Perception. Biotechniques 29: 832–843 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor N (2005) Personal communication [Google Scholar]
- Taylor N, Chavarriaga P, Raemakers K, Siritunga D, Zhang P (2004) Development and application of transgenic technologies in cassava. Plant Mol. Biol. 56: 671–688 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor SL, Lemanske RF, Bush RK, Busses WW (1987) Food Allergens: Structure and Immunologic Properties. Ann. Allergy 59: 93–99 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson CJ, Movva NR, Tizard R, Crameri R, Davies JE, Lauwereys M, Botterman J (1987) Characterization of the herbicide-resistance gene bar from Streptomyces hygroscopicus. EMBO J. 6: 2519–2523 [Google Scholar]
- Van den Eede G, Aarts H, Buhk H-J, Corthier G, Flint HJ, Hammes W, Jacobsen B, Midvedt T, Van der Vossen J, von Wright A, Wackernagel W, Wilcks A (2004). The relevance of gene transfer to the safety of food and feed derived from GM plants. Food Chem. Toxicol. 42: 1127–1156 [Google Scholar]
- Waldron C, Murphy EB, Roberts JL, Gustafson GD, Armour SL and Malcom SK (1985) Resistance to hygromycin B – a new marker for plant transformation studies. Plant [Google Scholar]
- Mol. Biol. 5: 103–108 [Google Scholar]
- Westby A (2002) Cassava utilization, storage and small-scale processing. In Hillocks RJ, Thresh JM, Bellotti AC, eds, Cassava: Biology, Production and Utilization, CAB International, pp 281–300 [Google Scholar]
- Wohlleben W, Arnold W, Broer I, Hilleman D, Struach E, Puhler A (1988) Nucleotide sequence of the phosphinothricin N-acetyltransferase gene from Streptomyces viridochromogenes Tu494 and its expression in Nicotiana tabacum. Gene 70: 25–37 [Google Scholar]
- Wolfenbarger LL, Phifer PR (2000) The ecological risks and benefits of genetically engineered plants. Science 290: 2088–2093 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (1993) Health aspects of marker genes in genetically modified plants: report of a WHO workshop, WHO/FNU/FOS/93.6 [Google Scholar]
- Zhang P, Legris G, Coulin P, Puonti-Kaerlas J (2000a) Production of stably transformed cassava plants via particle bombardment. Plant Cell Rep. 19: 939–945 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang P, Potrykus I, Puonti-Kaerlas J (2000b) Efficient production of transgenic cassava using negative and positive selection. Transgenic Res. 9: 405–415 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


